
Note: when putting the url for API, make sensable url name (for example: /students means we will get or deal with students data).
Directory Structure
Create a structure like this
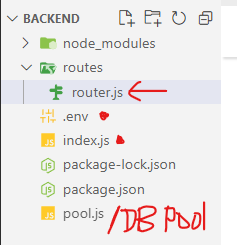
Setup an Express App
Install everything
Create a Backend Folder. Then open the folder with VS Code. (Note: If using Main Folder, then do ‘cd BACKEND’)
run this:
npm i express mysql2 dotenv nodemon
Create ENV FILE
create “.env” file (do npm i dotenv if you haven’t installed env)
type these:
MYSQL_HOST= check your connection in workbench, it will say 'localhost'
MYSQL_USER= check the same connection, it will say 'root'
MYSQL_PASSWORD= password of MySQL Workbench you written in diary/any paper
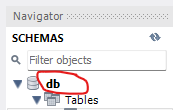
MYSQL_DATABASE= After opening workbench, See the database name there 'db' 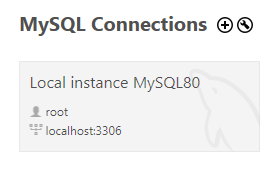
How to use these env, read it there. [link of that article]
Now Create An Express App with index.js
first create “index.js”
// index.js
require("dotenv").config()
const express=require('express')
const app =express()
app.get('/', (req, res)=>{
res.send('Backend successfully runned')
})
const PORT = 8000
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Backend Server is running on port ${PORT}`)
});START THE SERVER
Run using nodemon: npx nodemon index.js
or simply: node index.js
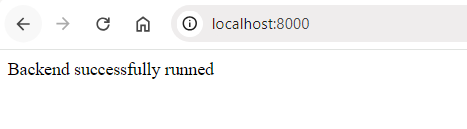
Now Open localhost:8000 in browser
# Create a MySQL Table
open mysql workbench
- Create a new schema
- Create a table
- Create fields ………… (fields, datatype, nn, pk, ai) (nn-not null, ai-auto increase)
- Right click the table and select all rows
- Fill the data
Create MySQL DB POOL ( //pool.js )
// pool.js
const mysql = require('mysql2');
const pool = mysql.createPool({
host: process.env.MYSQL_HOST,
user: process.env.MYSQL_USER,
password: process.env.MYSQL_PASSWORD,
database: process.env.MYSQL_DATABASE,
waitForConnections: true,
connectionLimit: 10, // Maximum number of connections in the pool
queueLimit: 0, // 0 means no limit for the queue
});
console.log('MySQL Pool created successfully.'); // Check if the pool is created successfully
// Test a connection from the pool
pool.getConnection((err, connection) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Testing: Error connecting to MySQL Pool:', err);
return;
}
console.log('Testing: Successfully connected to MySQL Pool');
// Release the connection back to the pool
connection.release();
});
module.exports = pool; // Export the poolImport the Pool ( // index.js )
const pool = require('./pool.js')Use Pool in index.js (Main File)
You probably don’t need it
In your index.js (or app.js), also import the pool from db.js if you need it in the main file. If you don’t need to use the pool in index.js, you don’t need to import it there.
How to use Pool in any Router? Just import it : )
const pool = require('./../pool.js')Output:
Create DELETE Route
create a file in
├── /routes
│ └── routerProduct.js
// routerProduct.js
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const pool = require('./../pool.js'); // Import the pool
// DELETE route to delete a product by ID
router.delete('/api/productlist/:id', (req, res) => {
const productId = req.params.id; // Get product ID from request parameters
const query = 'DELETE FROM table_name WHERE id = ?'; // SQL query to delete product
pool.query(query, [productId], (err, results) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Error occurred while deleting product:', err); // Log error details
return res.status(500).json({ message: 'Failed to delete product', error: err });
}
if (results.affectedRows === 0) {
// No product found with the given ID
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Product not found' });
}
console.log('Product deleted successfully:', results); // Log success message
res.status(200).json({ message: 'Product deleted successfully' });
});
});
module.exports = router;
// index.js
// Add routes
const routerProduct = require('./routes/routerProduct')
app.use(routerProduct)
// Middleware to parse JSON
app.use(express.json());






