Tissue Culture helps New Plants grow from its Tissue—super important for the mass production of plants and conservation of endangered species.
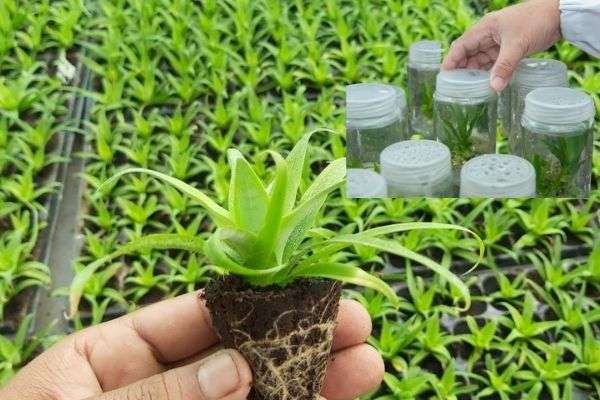

In this era of technology, many new and unique methods are invented to grow new plants. Among them, Tissue Culture is the most advanced technology for growing new plants.
It helps to grow new plants just from the tissue of an existing plant, allows better and faster growth of plants than the normal growing plant. Not only this, but we can also save the near extinction plant species through it.
This eliminates the need for seeds and has helped researchers avoid the problems of cross-pollination. These all benefits make tissue culture a very special topic.
So, Let’s get started!
What is Tissue Culture?
According to Scientific Approach, Tissue culture is a modern technique of vegetative propagation where a new plant is grown from a small piece of tissue.
Through tissue culture, we can grow an entire plant from a single cell and prepare clones of that exact same plant.
Science Behind Tissue Culture
So, you may ask, how does tissue culture work?
Its so simple, a plant has many cells and each cell contains DNA of whole plant from its structure to the proper growth and coordination.
In 1885, German Zoologist Wilhelm Roux conducted a experiment, he cultivated tissue from a chick embryo in a warm salt solution. He proved that each cell can grow into a new plant or a new animal when proper environment and nutrition are supplied.
Cells are isolated from plants or animals and grown in vitro (in glass containers).
Then the cells multiply themselves and grow into a baby plant.
How is tissue culture done?
In this process, you have to take a tiny piece of tissue from an existing plant and grow it in their lab or greenhouse.
First, the plant is cut into small pieces with some tissues.
Second, we have to place them into a nutrient-rich solution. The solution is constantly circulated to ensure that the tissue is in the right conditions to grow.
Third, we have to keep them in an artificial environment, so they can grow independently into full-size plants.
The new pieces of tissue are kept in sterile conditions until growth is complete.
They use a special solution for all stages of growth, including rooting, growing further, and growing into full plants.
Once the new plants grow, they’re transplanted into bigger pots and eventually back into the ground to live a long life.
Pros of Tissue Culture
- Many plants can be grown in a short period from their tissue parts.
- It helps to make identical copies of the parent plant.
- Healthy plants can be grown from disease-infected plants.
- Plants without seeds can be multiplied through tissue culture.
- It is very useful when sexual reproduction is not possible.
- These tissues can grow into new plants by giving them the right temperature and the right amount of nutrition.
- Tissue culture is helping to create healthier and more delicious food, which means people can eat more nutritiously.
- It allows scientists to grow cells that can be used for research, education, and technology development.
- We can save Near Extincting plant species through tissue culture.
Cons of Tissue Culture
- Tissue cultured plants have weak immunity when they are small.
- They need an artificial environment inside the lab.
- People with knowledge of tissue culture can only do this, not normal people.
- Due to the possession of the same genetic material, they can be resilient to environmental factors.
Conclusion
Scientists have figured out how to grow whole new plants from just a small bit of the actual plant using the process of tissue culture.
Plants grown in vitro can be genetically identical to the parent plant; this enables the production of transgenic plants and clones.
It is essential in the study of many different viruses and bacteria, as well as plant and animal cells.
It is often used in the manufacture of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and biopharmaceuticals.
In this blog, we will be exploring the process of tissue culture, as well as the future of tissue culture.
FAQs
What plants use tissue culture?
Actually, we can use tissue culture in all plants but at present it is used in specific plants for special purposes,
Mostly, the plants which use tissue culture are:
- Tomato
- Oil Palm
- Banana
- Rubber Tree
- Sweet Potato
What does it do?
The technology of tissue culture simply helps us to produce new plants from any tissue part of that plant.
Then that plant is moved to an artificial environment like labs for further growth and development.
When the plant grows big then that plant is now ready for plantation outside the artificial environment.
Now, you can plant them normally in pots or fields.
How is tissue culture used in agriculture?
Many propagators do farming of tissue culture in low investment and create higher revenue from it.
The reasons why tissue culture is used in agriculture are:
- Preservation of near extinction plant species
- Get an Identical copy of the plant
- Creating new disease-free-plants
- Improvement of plants from genetic variability
- Rapid production of new plants in a short time
- Develop more strong, healthy, and energetic plants
- Helping propagators to save money and increase revenue
How do tissue cultured plants look and taste?
Tissue cultured plants look the same as the parent plant because it is the identical clone of the parent plant.
These plants are healthy, tasty, and have much higher nutritional value than expected.
How do tissue culture plants differ from genetically modified plants?
Tissue culture plants are made from small tissues of that plant not by altering DNA.
But genetically modified plants are made by altering their DNA to give traits like pest resistance, strong immunity, and high production capacity.
So, tissue culture plants completely differ from genetically modified plants.
How tissue culture produces new plants
Tissue culture, also known as in vitro propagation, is a procedure used to grow new plants from small pieces of plant tissue.
The small pieces of tissue are placed in sterile media, where they are kept moist and at the correct temperature for plant growth.
After about a week, the plant tissue begins to grow new plantlets, and eventually roots and stems.
These plantlets are then removed from the media and sent to a greenhouse to mature.
The entire process of tissue culture takes about 6 to 8 weeks.
In this way, tissue culture helps to produce new plants.
Why tissue culture seems to be the future of cloning
Cloning is a process that has been used for years and has been a major part of the agricultural industry for decades.
Tissue culture, however, has a larger impact on cloning than just an alternative to the traditional process of cloning.
The process of tissue culture is what allows for cloning to be possible in the first place.
Tissue culture is used to grow the cells that are used to clone an individual animal or plant.
Tissue culture is just as important to the cloning process as the original process of taking cells and growing them into an embryo.
In fact, the term “cloning” doesn’t even exist without the concept of tissue culture.
That’s why tissue culture seems to be the future of cloning.
Related:
[Oldest Immortal Jellyfish] : Secret Key To Immortality
Why Can’t Human Regenerate Limbs
Why Designer Baby is the Upcoming Future

![Moon Jellyfish has [ Hidden Secrets ] You don't know moon jellyfish](https://spaceupper.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/1-1-300x169.jpg)







