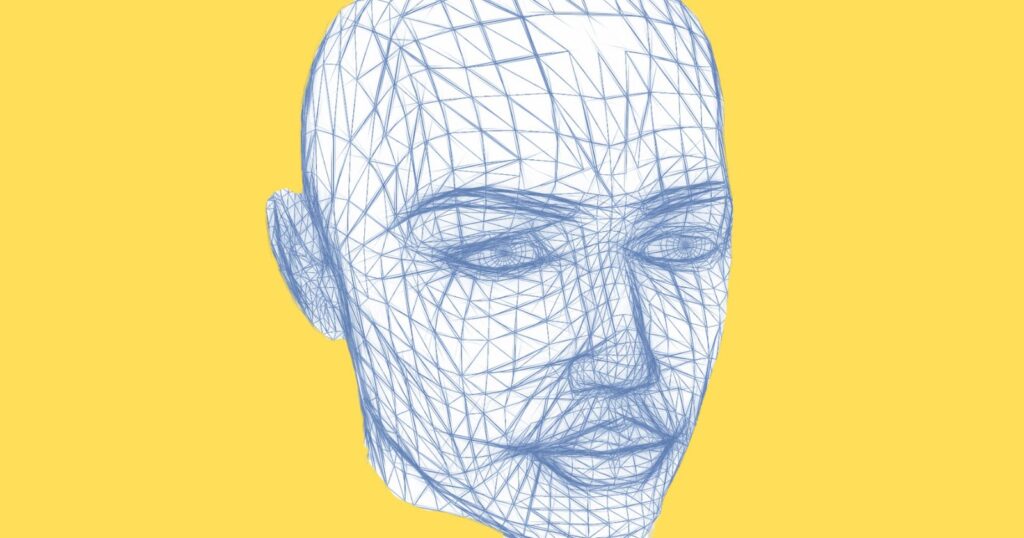
Facial recognition has progressed from being a mainstay of high-tech security systems in movies to being all about us and even in the palms of our hands in just a few decades.
In modern civilization, technology has been used in a variety of ways.
Some phones utilize face recognition to enable access, and countries such as China and the United States employ it on databases such as driver’s licenses for several purposes.
Then there are the entertaining Snapchat filters that use face detection.
Click to know: Google’s 3D Immersive View to Make You Fall in Love with Google Maps
Click to Know: 4 Ways AR Glasses Will Replace Smartphones – Easy Ultimate Guide
There is a significant distinction between face detection and facial recognition. With facial recognition, the computer says, “yes, that’s a face.” The computer says, “yes, that’s your face,” when using facial recognition.
Our brains catch up on this capacity to authenticate identification rather fast when we’re young, but it’s a fairly complicated challenge for computers. So, let’s look into face recognition and the science behind it.
When you think of a human face, you typically see a rather simple collection of traits. A face has three parts: eyes, a nose, and a mouth. However, there is more to a face than these traits.
In fact, to get a sense of how difficult this subject might become, sketch a variety of basic faces. They differ in many ways, such as the width of the nose, the distance between the eyes, the form and size of the lips, and so on.
Some facial recognition technology examines up to 80 aspects of the face to detect distinguishing traits and, ultimately, identities.
These traits become rather specific when the eye sockets’ depth, the cheekbones’ height, and the jawline’s curve are observed.
Of course, with so many specific elements to consider, difficulties might develop. Consider the issue of aging faces, for example. After all, as we age, our appearance changes.
To work around this, computers have learned certain aspects that remain essentially constant as people age, and they scrutinize these features thoroughly.
Even if we never aged, there would still be daily challenges.
What happens if the computer tries to analyze your face but you’re not always staring at its sensor or camera from the same angle?
This is something that people come up with regularly yet never have an issue with. However, for computers, this can create a significant challenge in identifying and recognizing faces.
Engineers have devised several methods to deal with this.
Many phones that use facial recognition may encourage you to move your face about when you set up the system to know what you look like from various angles.
Other systems use 2D-to-3D technology to translate a 2D picture of your face onto a 3D model to compute how you might appear from various perspectives.
Computers detect these characteristics on scales lower than a millimeter to create a “faceprint,” which is essentially a fingerprint for your face.
And these faceprints have grown quite precise. They can properly identify persons with near-perfect accuracy and even detect slight changes between identical twins.
As technology has advanced and becomes more widely available, so have the possibilities for its application.
Right now, we utilize face recognition for common purposes such as phone security, but the technology is seeing more serious applications from major institutions such as banks and even governments.
In Japan, several banks are considering incorporating face recognition technologies into their ATMs as a security safeguard for transaction verification.
Essential government agencies in the United States, such as ICE and the FBI, are employing face recognition to generate databases using existing papers such as driver’s licenses.
Whatever the use, we know that this technology is becoming increasingly prevalent in our daily lives, and it doesn’t appear that this will change anytime soon.
As with everything, we must be educated and informed about new technologies.
After all, they’re trying to learn everything they can about us.
ai is considered to be more threatening than quantum computing.
Click to know: What iPhones is Waterproof – 4 List of Best Water Resistant iPhones
Click to know: Are iPhone SE Waterproof? – 3 Ultimate Reasons For Waterproof Case





![Moon Jellyfish has [ Hidden Secrets ] You don't know moon jellyfish](https://spaceupper.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/1-1.jpg)
